2 major types of touch screens:
capacitive touch screen and resistive touch screen
Now, touch screens are most commonly used in human and machine interfaces (HMIs), for humans to control and interact by touch via finger, pen, and glove.
Given their characteristics, in the application of small-and-medium size screens, two major technologies are popular for their cost value and technical suitability: projected capacitive touch screens and resistive touch screens.
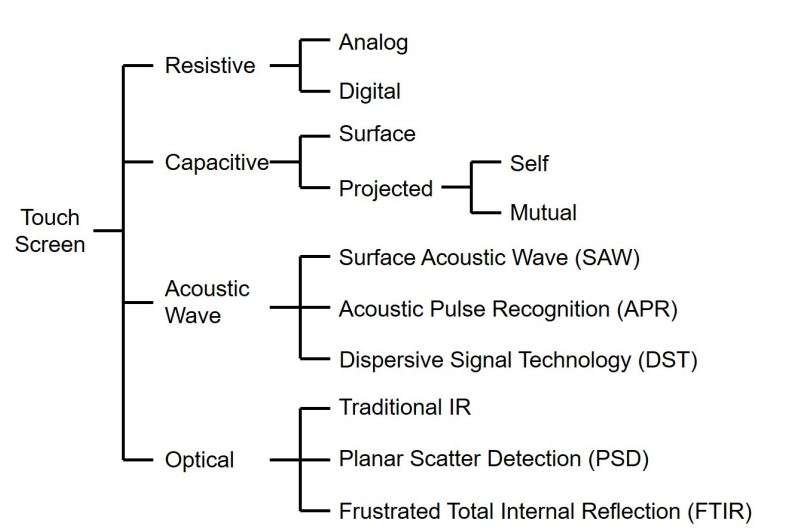
| Category | Resistive | Capacitive | Acoustic | Optical |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Size | Small | Small (ITO) Large (Metal Mesh) | Large | Large |
| Touch Diversity | High | Low | Average | High |
| Transmittance | 75-85% | 85-98% | 92-% | 88-% |
| Multi-touch | No (Analogy) Yes (Digital) | No (Surface, Self) Yes (Mutual) | No | No (Traditional) Yes (PSD, FTIR) |
| Durability | Poor | Good | Best | Best |
| Computational Power | Low | Average | High | Low (Traditional) High (PSD, FTIR) |
| Input Media | Finger/ Pressure Touch | Conductive Objects | Non-reflective Objects | Light-blocking Objects |
| Touch/Tap Force | Strong | Light | Average | Light |
| Resistance to Contaminants | Best | Poor | Good | Good |
| Production Cost | Low | High (Surface) Average (Projected) | High | High |
Table 1. Comparisons of touchscreen technologies: Resistive, Capacitive, Acoustic, Optical
How does touchscreen work?
Both types of touchscreens have their unique structure and operation technology, which decide their featured advantages and adoptions in different terminals.
Capacitive touchscreens: structure and operation principle
There are mainly 3 layers:
Sensor: it is a multi-layer composite screen. The inner surface and the interlayer of the screen are each coated with a conductive ITO layer, and ITO electrode patterns are deployed vertically and horizontally, and allow input with just a light touch of a finger.
In light of substrate, there are two types of sensors: film sensor and glass sensor.
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit): the connection between sensor and control IC; the connection between control IC and the host
ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) film: transparent conductive film, very thin, which is widely used due to its electrical conductivity and optical transparency.
Principle of operation:
- When touching the sensor screen with a finger, the electric field of the human body makes the finger and the touch screen surface form a coupling capacitance.
- The capacitance between the finger and the electrode changes as the finger approaches.
- The touch position is detected by examining the change in capacitance value between the vertical and horizontal electrodes.
More about the capacitive touch screen technology: “Capacitive Touch Screen “
Resistive touchscreens: structure and operation principle
There are mainly 3 layers:
Upper substrates with electrodes: film or glass attached to ITO film.
Lower substrates with electrodes: film or glass attached with ITO film, on top of which printed with insulating small protrusions (Dot Spacer).
Connector tail: the connection inserts between the upper and lower electrodes, for thermal fusion between the TP and the device.
Principle of operation:
- When touching the pressure load down the upper substrate, the upper and lower ITO electrodes (X/Y electrodes) contact and conduct each other to detect the input.
- The touch position is detected by measuring the change in voltage upon contact.
- The dot spacers between the upper and lower ITO electrodes are to prevent short-circuiting between the electrodes when no input is made.
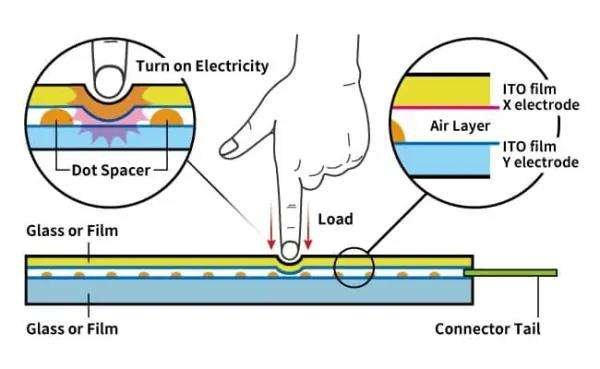
Capacitive Touchscreen vs. Resistive Touchscreen
Due to the flexibility in structure and touch function, capacitive touchscreens are the most popular type of touchscreen today.
However, the highly reliable and cost-benefit, resistive touch screens are still most common in many industrial applications, especially in manufacturing automation (MA).
Comparison in application:
| Capacitive Touch Panel | Resistive Touch Panel | |
| Advantage | · High durability · Multi-touch and gestures-touch · Improved design with cover-glass · Improved robustness with cover-glass · Flat surface design · Better visual quality in the high-lightness ambiance | · Any input media can be used · Low cost · Less susceptible to electrical noise · Less power consumption · Large tolerance in operational temperature |
| Disadvantage | · Influence of ambient noise causes malfunction · Higher cost than resistive film | · Durability is inferior to the capacitive method · Input needs to be thick · Scratch resistance is inferior to the CPT |
| Touch Function | One-touch, multi-touch, gestures-touch | Mostly one-touch, stylus pen, gloved-hand operation |
| Main Application | Smartphones, tablet PCs, car navigation systems, vending machines, wearable smart devices, office equipment, digital signage, electronic blackboards, arcade games | Industrial equipment, POS terminals, kiosks, mobile terminals, medical equipment, financial terminals, automatic teller machines, ATMs, ticket vending machines |
Common Custom Options
Our engineering team can design to accommodate the project requirement of function, budget, and product features to design the touchscreen with proper features.
Capacitive Touch Screen
| Structure | Touch function | Attaching Process Technology | Finish | Cover Glass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G+F, G+G, G+F+F | one-touch, multi-touch, gesture-touch | optical bonding to the LCD module, frame gluing(air bonding) to the LCD module | anti-glare, anti-fingerprint | material, thickness, surface hardness, surface finish |
Resistive Touch Screen
| Structure | Touch function | Finish | Connector |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-wire type 5-wire type | one-touch, gloved-hand operation | material, thickness, surface finish | FPC conversion |
Contact us for more development details.


